LBC Pap test
The Pap test is a quick and straightforward procedure in which a sample of cells is collected from the cervix. The sample is then sent to a cytology laboratory, where it is analyzed under a microscope. This allows early detection of changes that may indicate precancerous or cancerous conditions of the cervix.
Today, liquid-based cytology (LBC) is the most commonly used method. This advanced version of the traditional Pap smear collects and preserves the sample in a liquid medium, rather than manually smearing it onto a glass slide. LBC reduces the number of inadequate samples, improves the detection of abnormal cells, and enables simultaneous testing for HPV, providing more reliable and faster results in cervical cancer prevention.
If microscopic analysis reveals abnormal cells or signs of inflammation, the doctor may recommend further testing such as a repeat Pap test, microbiological tests, colposcopy, or biopsy.
The procedure is painless, lasts only a few minutes, and is the most critical method in secondary prevention/early detection of cervical cancer. It is recommended once a year for women undergoing treatment for precancerous changes, and, according to the gynecologist’s assessment, less frequently if results are expected.
Pap test recommendations
According to current guidelines in Croatia, the first Pap test is recommended after the onset of sexual activity, and no later than age 21 in sexually active women. If a woman is not sexually active, it can be postponed, but annual ultrasound check-ups and counseling are advised.
After that, Pap testing is recommended regularly according to age and previous results:
- Women 25–49 years: every three years
- Women 50–64 years: if previous results are expected, every three to five years
Recommendations may be adapted to individual circumstances, so it is best to consult a gynecologist.
The Pap test is a fundamental preventive examination in gynecology, as it can detect precancerous and cancerous changes at a very early stage—before symptoms appear—when treatment is simple and highly effective.
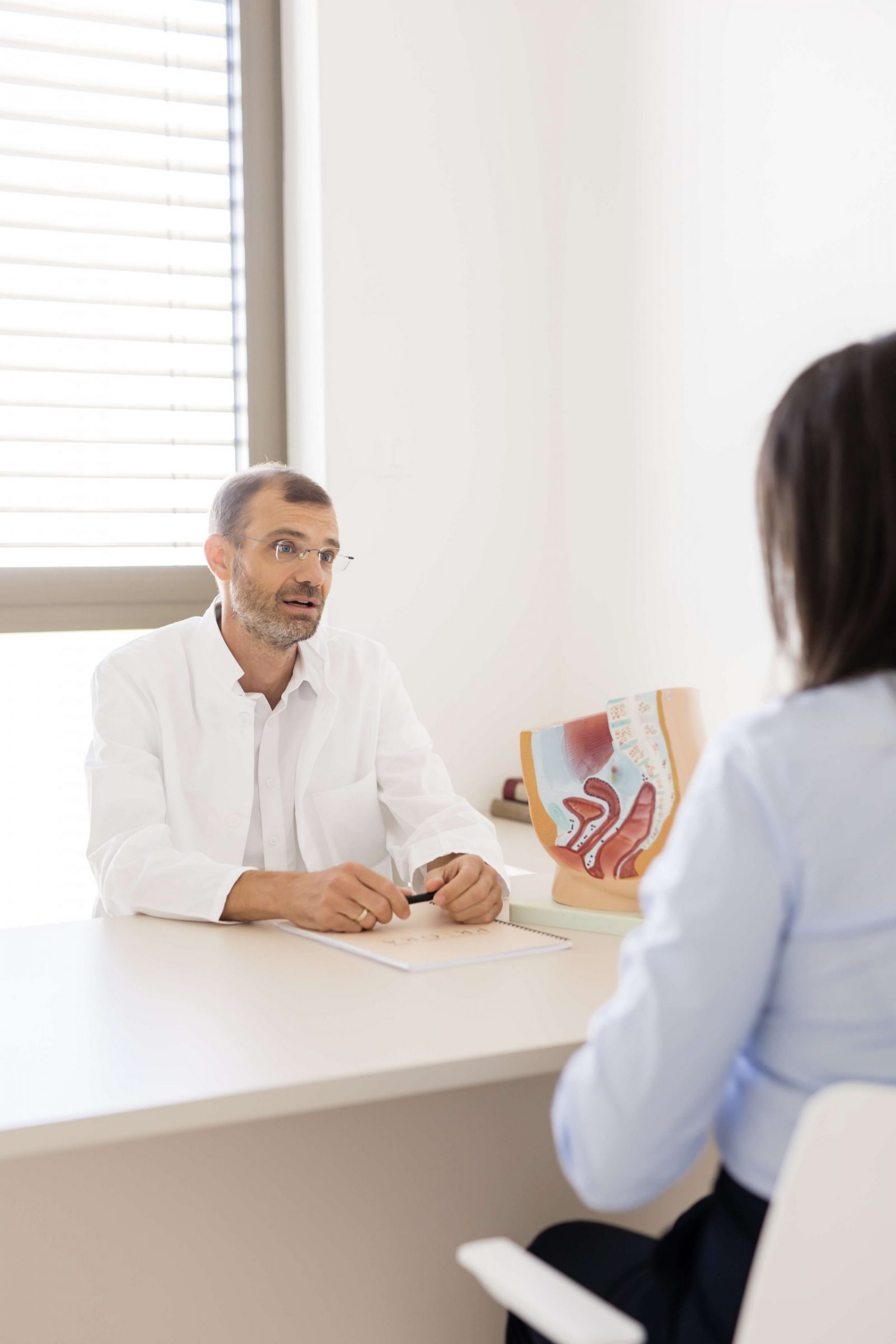


Dimitrije Milojković, MD
Medical team
With extensive experience in cervical cancer prevention, the gynecology team at IMC Priora performs PAP tests using state-of-the-art technology and an individualized approach to ensure early detection of changes, accurate diagnostics, and personalized care, raising the standards of prevention and women’s health protection.
